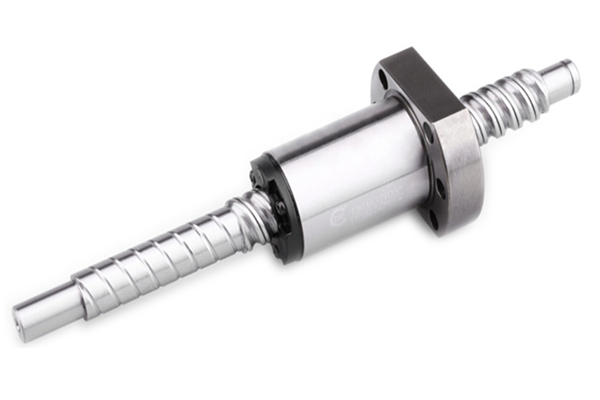
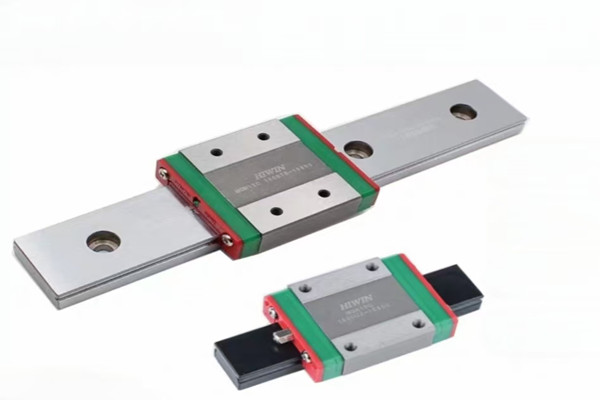
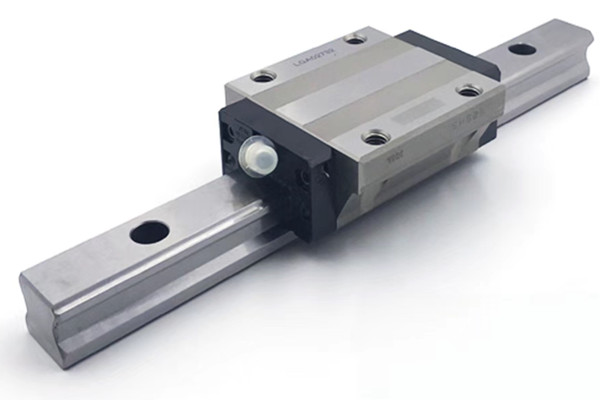
A linear shaft is a crucial component in many mechanical systems, acting as a supporting element that enables linear motion in machinery and devices. These shafts are often cylindrical rods or bars made from materials with high strength, durability, and resistance to wear, such as steel or stainless steel. They are primarily designed to support rotational or linear movement, making them indispensable in various applications ranging from industrial machinery to robotics and precision instruments.
What is a Linear Shaft?
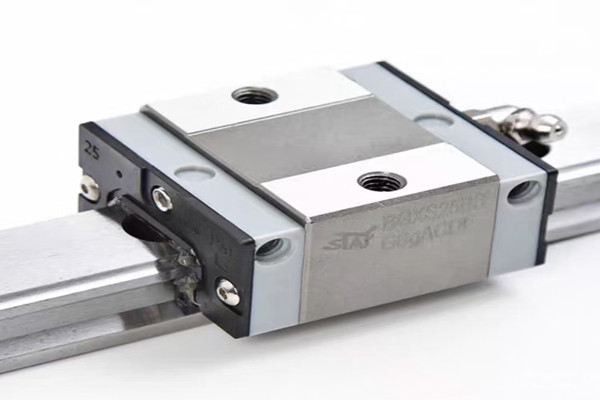
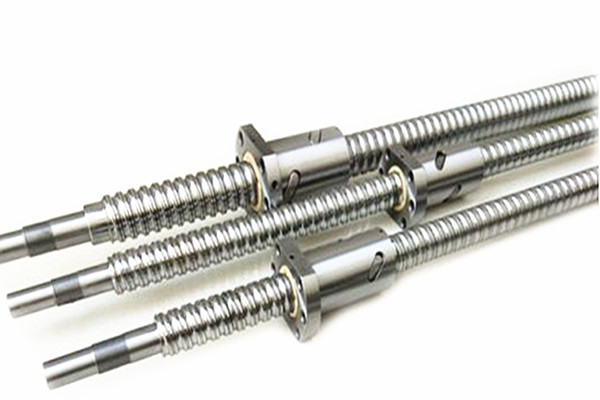
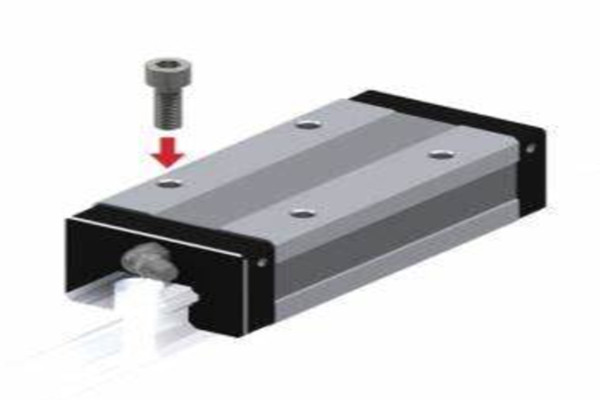
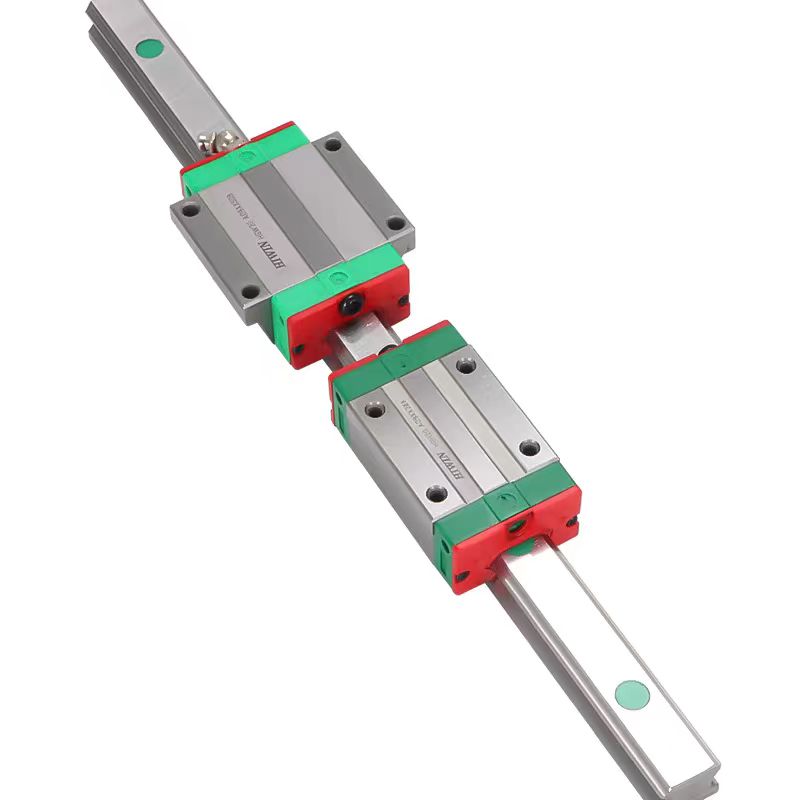
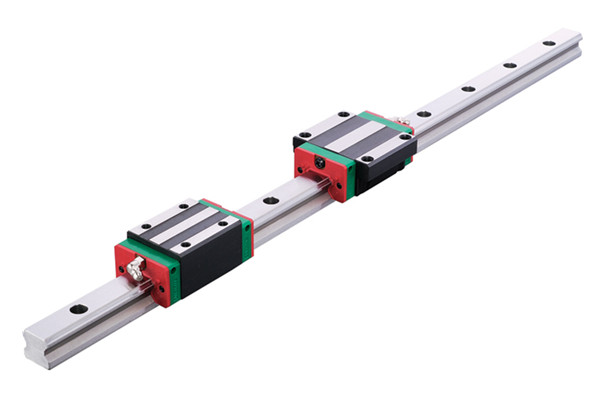
A linear shaft, also known as a guide shaft, is a mechanical component that serves as the axis along which a bearing or slider moves in a linear direction. In contrast to other types of shafts used in machinery, such as rotational shafts, a linear shaft’s primary function is to provide a stable track for components to move back and forth in a straight line. This motion can be either manually controlled or powered through motors or actuators.
In terms of design, a linear shaft is typically smooth and cylindrical, though the diameter and length may vary based on the specific application. Its surface is often hardened or precision-machined to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction between the shaft and the bearing components that slide along it.
Importance of Linear Shafts in Mechanical Systems
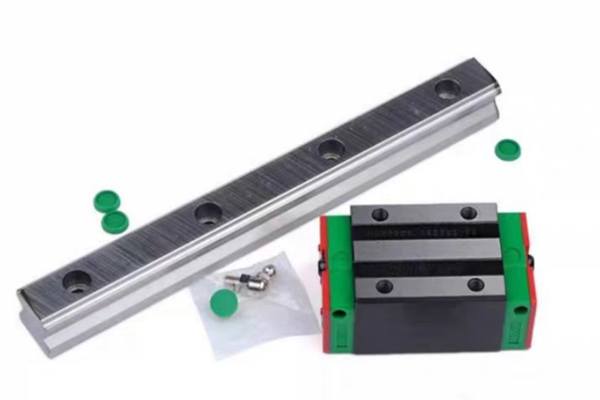
Linear shafts are vital in systems that require precise movement along a single axis. They are commonly used in conjunction with linear bearings or linear guides to ensure smooth, frictionless motion. This setup is integral to the design of machines like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines, 3D printers, and robotics, where precise, repeatable movements are essential for accurate performance.
One of the primary benefits of using linear shafts is the ability to achieve high precision. By ensuring that all moving parts are constrained to a single line of motion, linear shafts minimize errors caused by misalignment or irregular movements. Additionally, these shafts are often designed to handle heavy loads, providing support for substantial forces while maintaining smooth and consistent movement.
Applications of Linear Shafts
Linear shafts have a broad range of applications across various industries. In manufacturing and automation, they are frequently used in CNC machines, where they guide the cutting tools with pinpoint accuracy. Similarly, robotic arms use linear shafts to ensure that their joints or end-effectors can move with the required precision, particularly in tasks like assembly, inspection, or handling delicate materials.
In medical devices, linear shafts are often employed in equipment like infusion pumps, where the motion of critical components needs to be both smooth and accurate. Similarly, in optical instruments, such as microscopes or telescopes, linear shafts help guide components such as lenses or mirrors along the required axis, enabling precise adjustments.
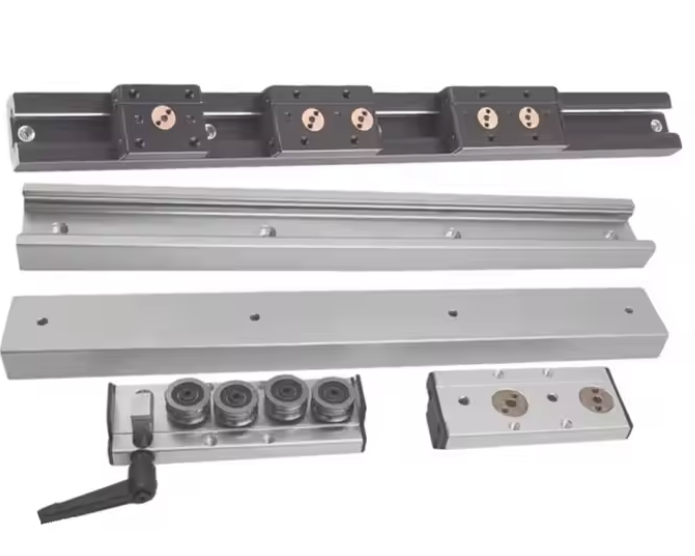
Types of Linear Shafts
There are several types of linear shafts, each designed for specific purposes:
Standard Linear Shafts: These are basic shafts that provide smooth, unrestricted motion. They are typically used in applications where the movement is straightforward and the load is relatively light.
Precision Linear Shafts: These shafts are manufactured to very tight tolerances and are used in high-precision applications. The surface finish is often enhanced to reduce friction and wear.
Hardened Linear Shafts: These shafts are heat-treated to achieve higher hardness, making them ideal for applications that involve higher stress or wear, such as in heavy machinery or industrial equipment.
Non-rotational Linear Shafts: These shafts are specifically designed to guide motion in one direction without rotation. They are commonly used in systems that require linear travel, such as sliding doors, linear actuators, or material handling systems.
Maintenance and Durability
Like any mechanical component, linear shafts require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. The most common issues encountered include wear and tear from friction, as well as corrosion from exposure to moisture or chemicals. To address these problems, many linear shafts are coated with lubricants or treated with anti-corrosive materials. Regular cleaning and inspection can help extend the life of these components and ensure that they continue to operate smoothly.
Xi’an Areswin Precision Machinery Company is leading sell the of linear shaft, material is carton steel and high precision. We can machining the shaft base on clients need. Please contact us for more information: https://www.aresmotion.com/product/linear-shaft/
Conclusion
The linear shaft is a fundamental component in modern mechanical systems, providing stability, precision, and support for linear motion. From industrial machines to robotics and medical devices, linear shafts are essential for ensuring smooth, controlled movement in a variety of applications. With the right design, material, and maintenance, these shafts can offer excellent performance and durability, making them indispensable in a wide range of industries.